Note
Click here to download the full example code
Tutorial 5: Colors and colorbars
This tutorial demonstrates how to configure the colorbar(s) with surfplot.
Layer color maps and colorbars
The color map can be specified for each added plotting layer using the cmap
parameter of add_layer(), along with the
associated matplotlib colorbar drawn if specified. The colobar can be
turned off by cbar=False. The range of the colormap is specified with the
color_range parameter, which takes a tuple of (minimum, maximum) values.
If no color range is specified (the default, i.e. None), then the color range
is computed automically based on the minimum and maximum of the data.
Let’s get started by setting up a plot with surface shading added as well. Following the first initial steps of Tutorial 1: Quick Start :
from neuromaps.datasets import fetch_fslr
from surfplot import Plot
surfaces = fetch_fslr()
lh, rh = surfaces['inflated']
p = Plot(lh, rh)
sulc_lh, sulc_rh = surfaces['sulc']
p.add_layer({'left': sulc_lh, 'right': sulc_rh}, cmap='binary_r', cbar=False)
Now let’s add a plotting layer with a colorbar using the example data. The
cmap parameter accepts any named matplotlib colormap, or a
colormap object. This means that surfplot can work with pretty much
any colormap, including those from seaborn and cmasher, for example.
from surfplot.datasets import load_example_data
# default mode network associations
default = load_example_data(join=True)
p.add_layer(default, cmap='GnBu_r', cbar_label='Default mode')
fig = p.build()
fig.show()
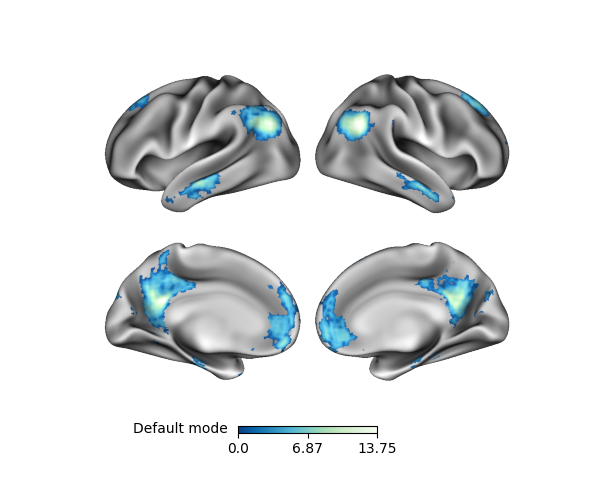
cbar_label added a text label to the colorbar. Although not necessary in
cases where a single layer/colorbar is shown, it can be useful when adding
multiple layers. To demonstrate that, let’s add another layer using the
frontoparietal network associations from
load_example_data():
fronto = load_example_data('frontoparietal', join=True)
p.add_layer(fronto, cmap='YlOrBr_r', cbar_label='Frontoparietal')
fig = p.build()
fig.show()
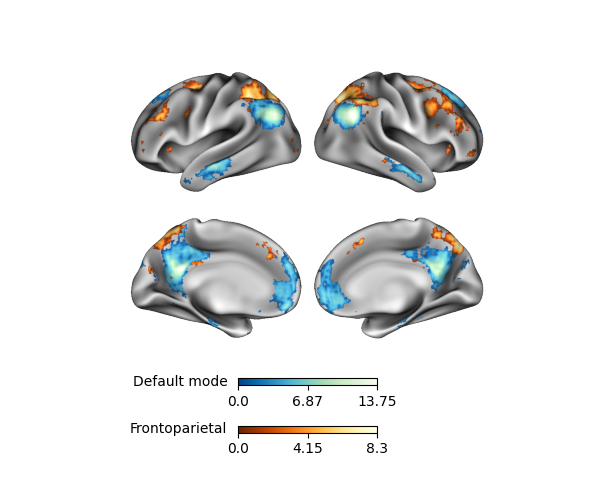
The order of the colorbars is always based on the order of the layers, where the outermost colorbar is the last (i.e. uppermost) plotting layer. Of course, more layers and colorbars can lead to busy-looking figure, so be sure not to overdo it.
cbar_kws
Once all layers have been added, the positioning and style can be adjusted
using the cbar_kws parameter in build(),
which are keyword arguments for surfplot.plotting.Plot._add_colorbars().
Each one is briefly described below (see _add_colorbars()
for more detail):
location: The location, relative to the surface plot
label_direction: Angle to draw label for colorbars
n_ticks: Number of ticks to include on colorbar
decimals: Number of decimals to show for colorbal tick values
fontsize: Font size for colorbar labels and tick labels
draw_border: Draw ticks and black border around colorbar
outer_labels_only: Show tick labels for only the outermost colorbar
aspect: Ratio of long to short dimensions
pad: Space that separates each colorbar
shrink: Fraction by which to multiply the size of the colorbar
fraction: Fraction of original axes to use for colorbar
Let’s plot colorbars on the right, which will generate vertical colorbars instead of horizontal colorbars. We’ll also add some style changes for a cleaner look:
kws = {'location': 'right', 'label_direction': 45, 'decimals': 1,
'fontsize': 8, 'n_ticks': 2, 'shrink': .15, 'aspect': 8,
'draw_border': False}
fig = p.build(cbar_kws=kws)
fig.show()
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 3
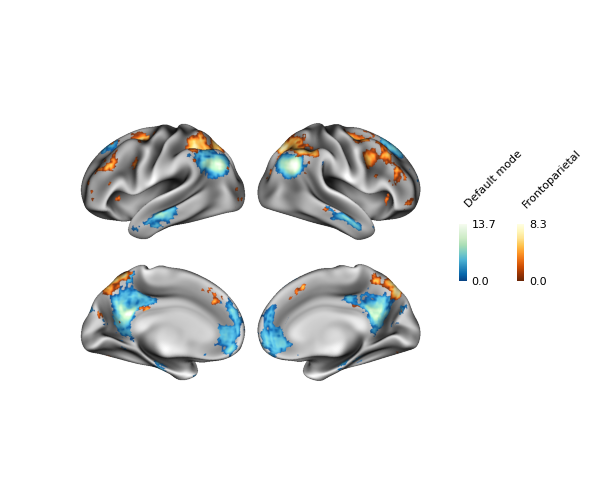
Be sure to check out Example 1: Multiple Stat Maps for another example of colorbar styling.
Transparency
The transparency of the plotting layers can be adjusted by the alpha
parameter. This may be preferred in cases with overlapping plotting layers.
We can recreate the example above with transparent maps like so:
p = Plot(lh, rh)
p.add_layer({'left': sulc_lh, 'right': sulc_rh}, cmap='binary_r', cbar=False)
p.add_layer(default, cmap='GnBu_r', cbar_label='Default mode', alpha=.5)
p.add_layer(fronto, cmap='YlOrBr_r', cbar_label='Frontoparietal', alpha=.5)
fig = p.build(cbar_kws=kws)
fig.show()
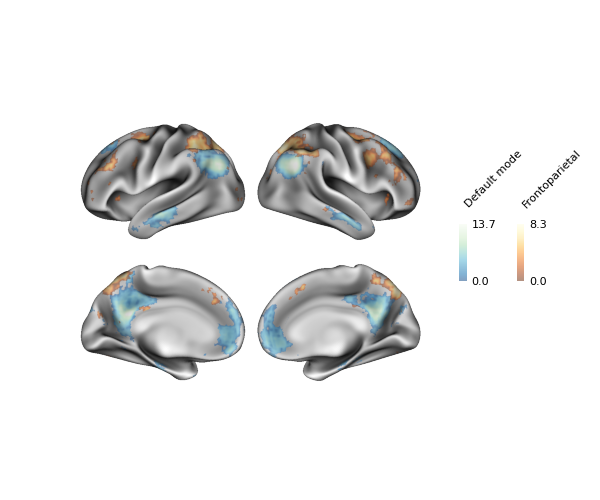
Although these particular maps are largely non-overlapping, you can see some small overlap at the edges of the default mode and frontoparietal clusters thanks to the transparency.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.783 seconds)